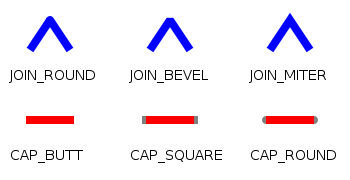
 *
* * The line cap and join styles can be set using the options illustrated * here: *
*  *
*
* A dash array can be used to specify lines with alternating opaque and
* transparent sections.
*/
public class BasicStroke implements Stroke
{
/**
* Indicates a mitered line join style. See the class overview for an
* illustration.
*/
public static final int JOIN_MITER = 0;
/**
* Indicates a rounded line join style. See the class overview for an
* illustration.
*/
public static final int JOIN_ROUND = 1;
/**
* Indicates a bevelled line join style. See the class overview for an
* illustration.
*/
public static final int JOIN_BEVEL = 2;
/**
* Indicates a flat line cap style. See the class overview for an
* illustration.
*/
public static final int CAP_BUTT = 0;
/**
* Indicates a rounded line cap style. See the class overview for an
* illustration.
*/
public static final int CAP_ROUND = 1;
/**
* Indicates a square line cap style. See the class overview for an
* illustration.
*/
public static final int CAP_SQUARE = 2;
/** The stroke width. */
private final float width;
/** The line cap style. */
private final int cap;
/** The line join style. */
private final int join;
/** The miter limit. */
private final float limit;
/** The dash array. */
private final float[] dash;
/** The dash phase. */
private final float phase;
// The inner and outer paths of the stroke
private Segment start, end;
/**
* Creates a new BasicStroke instance with the given attributes.
*
* @param width the line width (>= 0.0f).
* @param cap the line cap style (one of {@link #CAP_BUTT},
* {@link #CAP_ROUND} or {@link #CAP_SQUARE}).
* @param join the line join style (one of {@link #JOIN_ROUND},
* {@link #JOIN_BEVEL}, or {@link #JOIN_MITER}).
* @param miterlimit the limit to trim the miter join. The miterlimit must be
* greater than or equal to 1.0f.
* @param dash The array representing the dashing pattern. There must be at
* least one non-zero entry.
* @param dashPhase is negative and dash is not null.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If one input parameter doesn't meet
* its needs.
*/
public BasicStroke(float width, int cap, int join, float miterlimit,
float[] dash, float dashPhase)
{
if (width < 0.0f )
throw new IllegalArgumentException("width " + width + " < 0");
else if (cap < CAP_BUTT || cap > CAP_SQUARE)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("cap " + cap + " out of range ["
+ CAP_BUTT + ".." + CAP_SQUARE + "]");
else if (miterlimit < 1.0f && join == JOIN_MITER)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("miterlimit " + miterlimit
+ " < 1.0f while join == JOIN_MITER");
else if (join < JOIN_MITER || join > JOIN_BEVEL)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("join " + join + " out of range ["
+ JOIN_MITER + ".." + JOIN_BEVEL
+ "]");
else if (dashPhase < 0.0f && dash != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("dashPhase " + dashPhase
+ " < 0.0f while dash != null");
else if (dash != null)
if (dash.length == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("dash.length is 0");
else
{
boolean allZero = true;
for ( int i = 0; i < dash.length; ++i)
{
if (dash[i] != 0.0f)
{
allZero = false;
break;
}
}
if (allZero)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("all dashes are 0.0f");
}
this.width = width;
this.cap = cap;
this.join = join;
limit = miterlimit;
this.dash = dash == null ? null : (float[]) dash.clone();
phase = dashPhase;
}
/**
* Creates a new BasicStroke instance with the given attributes.
*
* @param width the line width (>= 0.0f).
* @param cap the line cap style (one of {@link #CAP_BUTT},
* {@link #CAP_ROUND} or {@link #CAP_SQUARE}).
* @param join the line join style (one of {@link #JOIN_ROUND},
* {@link #JOIN_BEVEL}, or {@link #JOIN_MITER}).
* @param miterlimit the limit to trim the miter join. The miterlimit must be
* greater than or equal to 1.0f.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If one input parameter doesn't meet
* its needs.
*/
public BasicStroke(float width, int cap, int join, float miterlimit)
{
this(width, cap, join, miterlimit, null, 0);
}
/**
* Creates a new BasicStroke instance with the given attributes.
* The miter limit defaults to 10.0.
*
* @param width the line width (>= 0.0f).
* @param cap the line cap style (one of {@link #CAP_BUTT},
* {@link #CAP_ROUND} or {@link #CAP_SQUARE}).
* @param join the line join style (one of {@link #JOIN_ROUND},
* {@link #JOIN_BEVEL}, or {@link #JOIN_MITER}).
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If one input parameter doesn't meet
* its needs.
*/
public BasicStroke(float width, int cap, int join)
{
this(width, cap, join, 10, null, 0);
}
/**
* Creates a new BasicStroke instance with the given line
* width. The default values are:
*
10.0f.
* width is negative.
*/
public BasicStroke(float width)
{
this(width, CAP_SQUARE, JOIN_MITER, 10, null, 0);
}
/**
* Creates a new BasicStroke instance. The default values are:
* 1.0f;10.0f.
* null, a continuous line will be drawn.
*
* @return The dash array (possibly null).
*/
public float[] getDashArray()
{
return dash;
}
/**
* Returns the dash phase for the stroke. This is the offset from the start
* of a path at which the pattern defined by {@link #getDashArray()} is
* rendered.
*
* @return The dash phase.
*/
public float getDashPhase()
{
return phase;
}
/**
* Returns the hash code for this object. The hash is calculated by
* xoring the hash, cap, join, limit, dash array and phase values
* (converted to int first with
* Float.floatToIntBits() if the value is a
* float).
*
* @return The hash code.
*/
public int hashCode()
{
int hash = Float.floatToIntBits(width);
hash ^= cap;
hash ^= join;
hash ^= Float.floatToIntBits(limit);
if (dash != null)
for (int i = 0; i < dash.length; i++)
hash ^= Float.floatToIntBits(dash[i]);
hash ^= Float.floatToIntBits(phase);
return hash;
}
/**
* Compares this BasicStroke for equality with an arbitrary
* object. This method returns true if and only if:
* o is an instanceof BasicStroke;o.null permitted).
*
* @return true if this stroke is equal to o and
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (! (o instanceof BasicStroke))
return false;
BasicStroke s = (BasicStroke) o;
return width == s.width && cap == s.cap && join == s.join
&& limit == s.limit && Arrays.equals(dash, s.dash) && phase == s.phase;
}
private Shape solidStroke(PathIterator pi)
{
double[] coords = new double[6];
double x, y, x0, y0;
boolean pathOpen = false;
GeneralPath output = new GeneralPath( );
Segment[] p;
x = x0 = y = y0 = 0;
while( !pi.isDone() )
{
switch( pi.currentSegment(coords) )
{
case PathIterator.SEG_MOVETO:
x0 = x = coords[0];
y0 = y = coords[1];
if( pathOpen )
{
capEnds();
convertPath(output, start);
start = end = null;
pathOpen = false;
}
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_LINETO:
p = (new LineSegment(x, y, coords[0], coords[1])).
getDisplacedSegments(width/2.0);
if( !pathOpen )
{
start = p[0];
end = p[1];
pathOpen = true;
}
else
addSegments(p);
x = coords[0];
y = coords[1];
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_QUADTO:
p = (new QuadSegment(x, y, coords[0], coords[1], coords[2],
coords[3])).getDisplacedSegments(width/2.0);
if( !pathOpen )
{
start = p[0];
end = p[1];
pathOpen = true;
}
else
addSegments(p);
x = coords[2];
y = coords[3];
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_CUBICTO:
p = new CubicSegment(x, y, coords[0], coords[1],
coords[2], coords[3],
coords[4], coords[5]).getDisplacedSegments(width/2.0);
if( !pathOpen )
{
start = p[0];
end = p[1];
pathOpen = true;
}
else
addSegments(p);
x = coords[4];
y = coords[5];
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_CLOSE:
if (x == x0 && y == y0)
{
joinSegments(new Segment[] { start.first, end.first });
}
else
{
p = (new LineSegment(x, y, x0, y0)).getDisplacedSegments(width / 2.0);
addSegments(p);
}
convertPath(output, start);
convertPath(output, end);
start = end = null;
pathOpen = false;
output.setWindingRule(GeneralPath.WIND_EVEN_ODD);
break;
}
pi.next();
}
if( pathOpen )
{
capEnds();
convertPath(output, start);
}
return output;
}
private Shape dashedStroke(PathIterator pi)
{
// The choice of (flatnessSq == width / 3) is made to be consistent with
// the flattening in CubicSegment.getDisplacedSegments
FlatteningPathIterator flat = new FlatteningPathIterator(pi,
Math.sqrt(width / 3));
// Holds the endpoint of the current segment (or piece of a segment)
double[] coords = new double[2];
// Holds end of the last segment
double x, y, x0, y0;
x = x0 = y = y0 = 0;
// Various useful flags
boolean pathOpen = false;
boolean dashOn = true;
boolean offsetting = (phase != 0);
// How far we are into the current dash
double distance = 0;
int dashIndex = 0;
// And variables to hold the final output
GeneralPath output = new GeneralPath();
Segment[] p;
// Iterate over the FlatteningPathIterator
while (! flat.isDone())
{
switch (flat.currentSegment(coords))
{
case PathIterator.SEG_MOVETO:
x0 = x = coords[0];
y0 = y = coords[1];
if (pathOpen)
{
capEnds();
convertPath(output, start);
start = end = null;
pathOpen = false;
}
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_LINETO:
boolean segmentConsumed = false;
while (! segmentConsumed)
{
// Find the total remaining length of this segment
double segLength = Math.sqrt((x - coords[0]) * (x - coords[0])
+ (y - coords[1])
* (y - coords[1]));
boolean spanBoundary = true;
double[] segmentEnd = null;
// The current segment fits entirely inside the current dash
if ((offsetting && distance + segLength <= phase)
|| distance + segLength <= dash[dashIndex])
{
spanBoundary = false;
}
// Otherwise, we need to split the segment in two, as this
// segment spans a dash boundry
else
{
segmentEnd = (double[]) coords.clone();
// Calculate the remaining distance in this dash,
// and coordinates of the dash boundary
double reqLength;
if (offsetting)
reqLength = phase - distance;
else
reqLength = dash[dashIndex] - distance;
coords[0] = x + ((coords[0] - x) * reqLength / segLength);
coords[1] = y + ((coords[1] - y) * reqLength / segLength);
}
if (offsetting || ! dashOn)
{
// Dash is off, or we are in offset - treat this as a
// moveTo
x0 = x = coords[0];
y0 = y = coords[1];
if (pathOpen)
{
capEnds();
convertPath(output, start);
start = end = null;
pathOpen = false;
}
}
else
{
// Dash is on - treat this as a lineTo
p = (new LineSegment(x, y, coords[0], coords[1])).getDisplacedSegments(width / 2.0);
if (! pathOpen)
{
start = p[0];
end = p[1];
pathOpen = true;
}
else
addSegments(p);
x = coords[0];
y = coords[1];
}
// Update variables depending on whether we spanned a
// dash boundary or not
if (! spanBoundary)
{
distance += segLength;
segmentConsumed = true;
}
else
{
if (offsetting)
offsetting = false;
dashOn = ! dashOn;
distance = 0;
coords = segmentEnd;
if (dashIndex + 1 == dash.length)
dashIndex = 0;
else
dashIndex++;
// Since the value of segmentConsumed is still false,
// the next run of the while loop will complete the segment
}
}
break;
// This is a flattened path, so we don't need to deal with curves
}
flat.next();
}
if (pathOpen)
{
capEnds();
convertPath(output, start);
}
return output;
}
/**
* Cap the ends of the path (joining the start and end list of segments)
*/
private void capEnds()
{
Segment returnPath = end.last;
end.reverseAll(); // reverse the path.
end = null;
capEnd(start, returnPath);
start.last = returnPath.last;
end = null;
capEnd(start, start);
}
/**
* Append the Segments in s to the GeneralPath p
*/
private void convertPath(GeneralPath p, Segment s)
{
Segment v = s;
p.moveTo((float)s.P1.getX(), (float)s.P1.getY());
do
{
if(v instanceof LineSegment)
p.lineTo((float)v.P2.getX(), (float)v.P2.getY());
else if(v instanceof QuadSegment)
p.quadTo((float)((QuadSegment)v).cp.getX(),
(float)((QuadSegment)v).cp.getY(),
(float)v.P2.getX(),
(float)v.P2.getY());
else if(v instanceof CubicSegment)
p.curveTo((float)((CubicSegment)v).cp1.getX(),
(float)((CubicSegment)v).cp1.getY(),
(float)((CubicSegment)v).cp2.getX(),
(float)((CubicSegment)v).cp2.getY(),
(float)v.P2.getX(),
(float)v.P2.getY());
v = v.next;
} while(v != s && v != null);
p.closePath();
}
/**
* Add the segments to start and end (the inner and outer edges of the stroke)
*/
private void addSegments(Segment[] segments)
{
joinSegments(segments);
start.add(segments[0]);
end.add(segments[1]);
}
private void joinSegments(Segment[] segments)
{
double[] p0 = start.last.cp2();
double[] p1 = new double[]{start.last.P2.getX(), start.last.P2.getY()};
double[] p2 = new double[]{segments[0].first.P1.getX(), segments[0].first.P1.getY()};
double[] p3 = segments[0].cp1();
Point2D p;
p = lineIntersection(p0[0],p0[1],p1[0],p1[1],
p2[0],p2[1],p3[0],p3[1], false);
double det = (p1[0] - p0[0])*(p3[1] - p2[1]) -
(p3[0] - p2[0])*(p1[1] - p0[1]);
if( det > 0 )
{
// start and segment[0] form the 'inner' part of a join,
// connect the overlapping segments
joinInnerSegments(start, segments[0], p);
joinOuterSegments(end, segments[1], p);
}
else
{
// end and segment[1] form the 'inner' part
joinInnerSegments(end, segments[1], p);
joinOuterSegments(start, segments[0], p);
}
}
/**
* Make a cap between a and b segments,
* where a-->b is the direction of iteration.
*/
private void capEnd(Segment a, Segment b)
{
double[] p0, p1;
double dx, dy, l;
Point2D c1,c2;
switch( cap )
{
case CAP_BUTT:
a.add(new LineSegment(a.last.P2, b.P1));
break;
case CAP_SQUARE:
p0 = a.last.cp2();
p1 = new double[]{a.last.P2.getX(), a.last.P2.getY()};
dx = p1[0] - p0[0];
dy = p1[1] - p0[1];
l = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
dx = 0.5*width*dx/l;
dy = 0.5*width*dy/l;
c1 = new Point2D.Double(p1[0] + dx, p1[1] + dy);
c2 = new Point2D.Double(b.P1.getX() + dx, b.P1.getY() + dy);
a.add(new LineSegment(a.last.P2, c1));
a.add(new LineSegment(c1, c2));
a.add(new LineSegment(c2, b.P1));
break;
case CAP_ROUND:
p0 = a.last.cp2();
p1 = new double[]{a.last.P2.getX(), a.last.P2.getY()};
dx = p1[0] - p0[0];
dy = p1[1] - p0[1];
if (dx != 0 && dy != 0)
{
l = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
dx = (2.0/3.0)*width*dx/l;
dy = (2.0/3.0)*width*dy/l;
}
c1 = new Point2D.Double(p1[0] + dx, p1[1] + dy);
c2 = new Point2D.Double(b.P1.getX() + dx, b.P1.getY() + dy);
a.add(new CubicSegment(a.last.P2, c1, c2, b.P1));
break;
}
a.add(b);
}
/**
* Returns the intersection of two lines, or null if there isn't one.
* @param infinite - true if the lines should be regarded as infinite, false
* if the intersection must be within the given segments.
* @return a Point2D or null.
*/
private Point2D lineIntersection(double X1, double Y1,
double X2, double Y2,
double X3, double Y3,
double X4, double Y4,
boolean infinite)
{
double x1 = X1;
double y1 = Y1;
double rx = X2 - x1;
double ry = Y2 - y1;
double x2 = X3;
double y2 = Y3;
double sx = X4 - x2;
double sy = Y4 - y2;
double determinant = sx * ry - sy * rx;
double nom = (sx * (y2 - y1) + sy * (x1 - x2));
// lines can be considered parallel.
if (Math.abs(determinant) < 1E-6)
return null;
nom = nom / determinant;
// check if lines are within the bounds
if(!infinite && (nom > 1.0 || nom < 0.0))
return null;
return new Point2D.Double(x1 + nom * rx, y1 + nom * ry);
}
/**
* Join a and b segments, where a-->b is the direction of iteration.
*
* insideP is the inside intersection point of the join, needed for
* calculating miter lengths.
*/
private void joinOuterSegments(Segment a, Segment b, Point2D insideP)
{
double[] p0, p1;
double dx, dy, l;
Point2D c1,c2;
switch( join )
{
case JOIN_MITER:
p0 = a.last.cp2();
p1 = new double[]{a.last.P2.getX(), a.last.P2.getY()};
double[] p2 = new double[]{b.P1.getX(), b.P1.getY()};
double[] p3 = b.cp1();
Point2D p = lineIntersection(p0[0],p0[1],p1[0],p1[1],p2[0],p2[1],p3[0],p3[1], true);
if( p == null || insideP == null )
a.add(new LineSegment(a.last.P2, b.P1));
else if((p.distance(insideP)/width) < limit)
{
a.add(new LineSegment(a.last.P2, p));
a.add(new LineSegment(p, b.P1));
}
else
{
// outside miter limit, do a bevel join.
a.add(new LineSegment(a.last.P2, b.P1));
}
break;
case JOIN_ROUND:
p0 = a.last.cp2();
p1 = new double[]{a.last.P2.getX(), a.last.P2.getY()};
dx = p1[0] - p0[0];
dy = p1[1] - p0[1];
l = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
dx = 0.5*width*dx/l;
dy = 0.5*width*dy/l;
c1 = new Point2D.Double(p1[0] + dx, p1[1] + dy);
p0 = new double[]{b.P1.getX(), b.P1.getY()};
p1 = b.cp1();
dx = p0[0] - p1[0]; // backwards direction.
dy = p0[1] - p1[1];
l = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
dx = 0.5*width*dx/l;
dy = 0.5*width*dy/l;
c2 = new Point2D.Double(p0[0] + dx, p0[1] + dy);
a.add(new CubicSegment(a.last.P2, c1, c2, b.P1));
break;
case JOIN_BEVEL:
a.add(new LineSegment(a.last.P2, b.P1));
break;
}
}
/**
* Join a and b segments, removing any overlap
*/
private void joinInnerSegments(Segment a, Segment b, Point2D p)
{
double[] p0 = a.last.cp2();
double[] p1 = new double[] { a.last.P2.getX(), a.last.P2.getY() };
double[] p2 = new double[] { b.P1.getX(), b.P1.getY() };
double[] p3 = b.cp1();
if (p == null)
{
// Dodgy.
a.add(new LineSegment(a.last.P2, b.P1));
p = new Point2D.Double((b.P1.getX() + a.last.P2.getX()) / 2.0,
(b.P1.getY() + a.last.P2.getY()) / 2.0);
}
else
// This assumes segments a and b are single segments, which is
// incorrect - if they are a linked list of segments (ie, passed in
// from a flattening operation), this produces strange results!!
a.last.P2 = b.P1 = p;
}
}