 *
* The inside of the curve is defined for drawing purposes by a winding * rule. Either the WIND_EVEN_ODD or WIND_NON_ZERO winding rule can be chosen. * *
 *
*
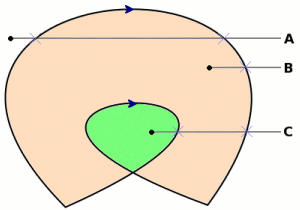
The EVEN_ODD winding rule defines a point as inside a path if: * A ray from the point towards infinity in an arbitrary direction * intersects the path an odd number of times. Points A and * C in the image are considered to be outside the path. * (both intersect twice) * Point B intersects once, and is inside. * *
The NON_ZERO winding rule defines a point as inside a path if:
* The path intersects the ray in an equal number of opposite directions.
* Point A in the image is outside (one intersection in the
* ’up’
* direction, one in the ’down’ direction) Point B in
* the image is inside (one intersection ’down’)
* Point C in the image is inside (two intersections in the
* ’down’ direction)
*
* @see Line2D
* @see CubicCurve2D
* @see QuadCurve2D
*
* @author Sascha Brawer (brawer@dandelis.ch)
* @author Sven de Marothy (sven@physto.se)
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public final class GeneralPath implements Shape, Cloneable
{
/** Same constant as {@link PathIterator#WIND_EVEN_ODD}. */
public static final int WIND_EVEN_ODD = PathIterator.WIND_EVEN_ODD;
/** Same constant as {@link PathIterator#WIND_NON_ZERO}. */
public static final int WIND_NON_ZERO = PathIterator.WIND_NON_ZERO;
/** Initial size if not specified. */
private static final int INIT_SIZE = 10;
/** A big number, but not so big it can't survive a few float operations */
private static final double BIG_VALUE = Double.MAX_VALUE / 10.0;
/** The winding rule.
* This is package-private to avoid an accessor method.
*/
int rule;
/**
* The path type in points. Note that xpoints[index] and ypoints[index] maps
* to types[index]; the control points of quad and cubic paths map as
* well but are ignored.
* This is package-private to avoid an accessor method.
*/
byte[] types;
/**
* The list of all points seen. Since you can only append floats, it makes
* sense for these to be float[]. I have no idea why Sun didn't choose to
* allow a general path of double precision points.
* Note: Storing x and y coords seperately makes for a slower transforms,
* But it speeds up and simplifies box-intersection checking a lot.
* These are package-private to avoid accessor methods.
*/
float[] xpoints;
float[] ypoints;
/** The index of the most recent moveto point, or null. */
private int subpath = -1;
/** The next available index into points.
* This is package-private to avoid an accessor method.
*/
int index;
/**
* Constructs a GeneralPath with the default (NON_ZERO)
* winding rule and initial capacity (20).
*/
public GeneralPath()
{
this(WIND_NON_ZERO, INIT_SIZE);
}
/**
* Constructs a GeneralPath with a specific winding rule
* and the default initial capacity (20).
* @param rule the winding rule ({@link #WIND_NON_ZERO} or
* {@link #WIND_EVEN_ODD})
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if rule is not one of the
* listed values.
*/
public GeneralPath(int rule)
{
this(rule, INIT_SIZE);
}
/**
* Constructs a GeneralPath with a specific winding rule
* and the initial capacity. The initial capacity should be
* the approximate number of path segments to be used.
* @param rule the winding rule ({@link #WIND_NON_ZERO} or
* {@link #WIND_EVEN_ODD})
* @param capacity the inital capacity, in path segments
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if rule is not one of the
* listed values.
*/
public GeneralPath(int rule, int capacity)
{
if (rule != WIND_EVEN_ODD && rule != WIND_NON_ZERO)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.rule = rule;
if (capacity < INIT_SIZE)
capacity = INIT_SIZE;
types = new byte[capacity];
xpoints = new float[capacity];
ypoints = new float[capacity];
}
/**
* Constructs a GeneralPath from an arbitrary shape object.
* The Shapes PathIterator path and winding rule will be used.
*
* @param s the shape (null not permitted).
*
* @throws NullPointerException if shape is null.
*/
public GeneralPath(Shape s)
{
types = new byte[INIT_SIZE];
xpoints = new float[INIT_SIZE];
ypoints = new float[INIT_SIZE];
PathIterator pi = s.getPathIterator(null);
setWindingRule(pi.getWindingRule());
append(pi, false);
}
/**
* Adds a new point to a path.
*
* @param x the x-coordinate.
* @param y the y-coordinate.
*/
public void moveTo(float x, float y)
{
subpath = index;
ensureSize(index + 1);
types[index] = PathIterator.SEG_MOVETO;
xpoints[index] = x;
ypoints[index++] = y;
}
/**
* Appends a straight line to the current path.
* @param x x coordinate of the line endpoint.
* @param y y coordinate of the line endpoint.
*/
public void lineTo(float x, float y)
{
ensureSize(index + 1);
types[index] = PathIterator.SEG_LINETO;
xpoints[index] = x;
ypoints[index++] = y;
}
/**
* Appends a quadratic Bezier curve to the current path.
* @param x1 x coordinate of the control point
* @param y1 y coordinate of the control point
* @param x2 x coordinate of the curve endpoint.
* @param y2 y coordinate of the curve endpoint.
*/
public void quadTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2)
{
ensureSize(index + 2);
types[index] = PathIterator.SEG_QUADTO;
xpoints[index] = x1;
ypoints[index++] = y1;
xpoints[index] = x2;
ypoints[index++] = y2;
}
/**
* Appends a cubic Bezier curve to the current path.
* @param x1 x coordinate of the first control point
* @param y1 y coordinate of the first control point
* @param x2 x coordinate of the second control point
* @param y2 y coordinate of the second control point
* @param x3 x coordinate of the curve endpoint.
* @param y3 y coordinate of the curve endpoint.
*/
public void curveTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3,
float y3)
{
ensureSize(index + 3);
types[index] = PathIterator.SEG_CUBICTO;
xpoints[index] = x1;
ypoints[index++] = y1;
xpoints[index] = x2;
ypoints[index++] = y2;
xpoints[index] = x3;
ypoints[index++] = y3;
}
/**
* Closes the current subpath by drawing a line
* back to the point of the last moveTo, unless the path is already closed.
*/
public void closePath()
{
if (index >= 1 && types[index - 1] == PathIterator.SEG_CLOSE)
return;
ensureSize(index + 1);
types[index] = PathIterator.SEG_CLOSE;
xpoints[index] = xpoints[subpath];
ypoints[index++] = ypoints[subpath];
}
/**
* Appends the segments of a Shape to the path. If connect is
* true, the new path segments are connected to the existing one with a line.
* The winding rule of the Shape is ignored.
*
* @param s the shape (null not permitted).
* @param connect whether to connect the new shape to the existing path.
*
* @throws NullPointerException if s is null.
*/
public void append(Shape s, boolean connect)
{
append(s.getPathIterator(null), connect);
}
/**
* Appends the segments of a PathIterator to this GeneralPath.
* Optionally, the initial {@link PathIterator#SEG_MOVETO} segment
* of the appended path is changed into a {@link
* PathIterator#SEG_LINETO} segment.
*
* @param iter the PathIterator specifying which segments shall be
* appended (null not permitted).
*
* @param connect true for substituting the initial
* {@link PathIterator#SEG_MOVETO} segment by a {@link
* PathIterator#SEG_LINETO}, or false for not
* performing any substitution. If this GeneralPath is currently
* empty, connect is assumed to be false,
* thus leaving the initial {@link PathIterator#SEG_MOVETO}
* unchanged.
*/
public void append(PathIterator iter, boolean connect)
{
// A bad implementation of this method had caused Classpath bug #6076.
float[] f = new float[6];
while (! iter.isDone())
{
switch (iter.currentSegment(f))
{
case PathIterator.SEG_MOVETO:
if (! connect || (index == 0))
{
moveTo(f[0], f[1]);
break;
}
if ((index >= 1) && (types[index - 1] == PathIterator.SEG_CLOSE)
&& (f[0] == xpoints[index - 1])
&& (f[1] == ypoints[index - 1]))
break;
// Fall through.
case PathIterator.SEG_LINETO:
lineTo(f[0], f[1]);
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_QUADTO:
quadTo(f[0], f[1], f[2], f[3]);
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_CUBICTO:
curveTo(f[0], f[1], f[2], f[3], f[4], f[5]);
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_CLOSE:
closePath();
break;
}
connect = false;
iter.next();
}
}
/**
* Returns the path’s current winding rule.
*
* @return {@link #WIND_EVEN_ODD} or {@link #WIND_NON_ZERO}.
*/
public int getWindingRule()
{
return rule;
}
/**
* Sets the path’s winding rule, which controls which areas are
* considered ’inside’ or ’outside’ the path
* on drawing. Valid rules are WIND_EVEN_ODD for an even-odd winding rule,
* or WIND_NON_ZERO for a non-zero winding rule.
*
* @param rule the rule ({@link #WIND_EVEN_ODD} or {@link #WIND_NON_ZERO}).
*/
public void setWindingRule(int rule)
{
if (rule != WIND_EVEN_ODD && rule != WIND_NON_ZERO)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.rule = rule;
}
/**
* Returns the current appending point of the path.
*
* @return The point.
*/
public Point2D getCurrentPoint()
{
if (subpath < 0)
return null;
return new Point2D.Float(xpoints[index - 1], ypoints[index - 1]);
}
/**
* Resets the path. All points and segments are destroyed.
*/
public void reset()
{
subpath = -1;
index = 0;
}
/**
* Applies a transform to the path.
*
* @param xform the transform (null not permitted).
*/
public void transform(AffineTransform xform)
{
double nx;
double ny;
double[] m = new double[6];
xform.getMatrix(m);
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
nx = m[0] * xpoints[i] + m[2] * ypoints[i] + m[4];
ny = m[1] * xpoints[i] + m[3] * ypoints[i] + m[5];
xpoints[i] = (float) nx;
ypoints[i] = (float) ny;
}
}
/**
* Creates a transformed version of the path.
* @param xform the transform to apply
* @return a new transformed GeneralPath
*/
public Shape createTransformedShape(AffineTransform xform)
{
GeneralPath p = new GeneralPath(this);
p.transform(xform);
return p;
}
/**
* Returns the path’s bounding box.
*/
public Rectangle getBounds()
{
return getBounds2D().getBounds();
}
/**
* Returns the path’s bounding box, in float precision
*/
public Rectangle2D getBounds2D()
{
float x1;
float y1;
float x2;
float y2;
if (index > 0)
{
x1 = x2 = xpoints[0];
y1 = y2 = ypoints[0];
}
else
x1 = x2 = y1 = y2 = 0.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
x1 = Math.min(xpoints[i], x1);
y1 = Math.min(ypoints[i], y1);
x2 = Math.max(xpoints[i], x2);
y2 = Math.max(ypoints[i], y2);
}
return (new Rectangle2D.Float(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1));
}
/**
* Evaluates if a point is within the GeneralPath,
* The NON_ZERO winding rule is used, regardless of the
* set winding rule.
* @param x x coordinate of the point to evaluate
* @param y y coordinate of the point to evaluate
* @return true if the point is within the path, false otherwise
*/
public boolean contains(double x, double y)
{
return (getWindingNumber(x, y) != 0);
}
/**
* Evaluates if a Point2D is within the GeneralPath,
* The NON_ZERO winding rule is used, regardless of the
* set winding rule.
* @param p The Point2D to evaluate
* @return true if the point is within the path, false otherwise
*/
public boolean contains(Point2D p)
{
return contains(p.getX(), p.getY());
}
/**
* Evaluates if a rectangle is completely contained within the path.
* This method will return false in the cases when the box
* intersects an inner segment of the path.
* (i.e.: The method is accurate for the EVEN_ODD winding rule)
*/
public boolean contains(double x, double y, double w, double h)
{
if (! getBounds2D().intersects(x, y, w, h))
return false;
/* Does any edge intersect? */
if (getAxisIntersections(x, y, false, w) != 0 /* top */
|| getAxisIntersections(x, y + h, false, w) != 0 /* bottom */
|| getAxisIntersections(x + w, y, true, h) != 0 /* right */
|| getAxisIntersections(x, y, true, h) != 0) /* left */
return false;
/* No intersections, is any point inside? */
if (getWindingNumber(x, y) != 0)
return true;
return false;
}
/**
* Evaluates if a rectangle is completely contained within the path.
* This method will return false in the cases when the box
* intersects an inner segment of the path.
* (i.e.: The method is accurate for the EVEN_ODD winding rule)
* @param r the rectangle
* @return true if the rectangle is completely contained
* within the path, false otherwise
*/
public boolean contains(Rectangle2D r)
{
return contains(r.getX(), r.getY(), r.getWidth(), r.getHeight());
}
/**
* Evaluates if a rectangle intersects the path.
* @param x x coordinate of the rectangle
* @param y y coordinate of the rectangle
* @param w width of the rectangle
* @param h height of the rectangle
* @return true if the rectangle intersects the path,
* false otherwise
*/
public boolean intersects(double x, double y, double w, double h)
{
/* Does any edge intersect? */
if (getAxisIntersections(x, y, false, w) != 0 /* top */
|| getAxisIntersections(x, y + h, false, w) != 0 /* bottom */
|| getAxisIntersections(x + w, y, true, h) != 0 /* right */
|| getAxisIntersections(x, y, true, h) != 0) /* left */
return true;
/* No intersections, is any point inside? */
if (getWindingNumber(x, y) != 0)
return true;
return false;
}
/**
* Evaluates if a Rectangle2D intersects the path.
* @param r The rectangle
* @return true if the rectangle intersects the path,
* false otherwise
*/
public boolean intersects(Rectangle2D r)
{
return intersects(r.getX(), r.getY(), r.getWidth(), r.getHeight());
}
/**
* A PathIterator that iterates over the segments of a GeneralPath.
*
* @author Sascha Brawer (brawer@dandelis.ch)
*/
private static class GeneralPathIterator implements PathIterator
{
/**
* The number of coordinate values for each segment type.
*/
private static final int[] NUM_COORDS = {
/* 0: SEG_MOVETO */ 1,
/* 1: SEG_LINETO */ 1,
/* 2: SEG_QUADTO */ 2,
/* 3: SEG_CUBICTO */ 3,
/* 4: SEG_CLOSE */ 0};
/**
* The GeneralPath whose segments are being iterated.
* This is package-private to avoid an accessor method.
*/
final GeneralPath path;
/**
* The affine transformation used to transform coordinates.
*/
private final AffineTransform transform;
/**
* The current position of the iterator.
*/
private int pos;
/**
* Constructs a new iterator for enumerating the segments of a
* GeneralPath.
*
* @param path the path to enumerate
* @param transform an affine transformation for projecting the returned
* points, or null to return the original points
* without any mapping.
*/
GeneralPathIterator(GeneralPath path, AffineTransform transform)
{
this.path = path;
this.transform = transform;
}
/**
* Returns the current winding rule of the GeneralPath.
*/
public int getWindingRule()
{
return path.rule;
}
/**
* Determines whether the iterator has reached the last segment in
* the path.
*/
public boolean isDone()
{
return pos >= path.index;
}
/**
* Advances the iterator position by one segment.
*/
public void next()
{
int seg;
/*
* Increment pos by the number of coordinate pairs.
*/
seg = path.types[pos];
if (seg == SEG_CLOSE)
pos++;
else
pos += NUM_COORDS[seg];
}
/**
* Returns the current segment in float coordinates.
*/
public int currentSegment(float[] coords)
{
int seg;
int numCoords;
seg = path.types[pos];
numCoords = NUM_COORDS[seg];
if (numCoords > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < numCoords; i++)
{
coords[i << 1] = path.xpoints[pos + i];
coords[(i << 1) + 1] = path.ypoints[pos + i];
}
if (transform != null)
transform.transform( /* src */
coords, /* srcOffset */
0, /* dest */ coords, /* destOffset */
0, /* numPoints */ numCoords);
}
return seg;
}
/**
* Returns the current segment in double coordinates.
*/
public int currentSegment(double[] coords)
{
int seg;
int numCoords;
seg = path.types[pos];
numCoords = NUM_COORDS[seg];
if (numCoords > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < numCoords; i++)
{
coords[i << 1] = (double) path.xpoints[pos + i];
coords[(i << 1) + 1] = (double) path.ypoints[pos + i];
}
if (transform != null)
transform.transform( /* src */
coords, /* srcOffset */
0, /* dest */ coords, /* destOffset */
0, /* numPoints */ numCoords);
}
return seg;
}
}
/**
* Creates a PathIterator for iterating along the segments of the path.
*
* @param at an affine transformation for projecting the returned
* points, or null to let the created iterator return
* the original points without any mapping.
*/
public PathIterator getPathIterator(AffineTransform at)
{
return new GeneralPathIterator(this, at);
}
/**
* Creates a new FlatteningPathIterator for the path
*/
public PathIterator getPathIterator(AffineTransform at, double flatness)
{
return new FlatteningPathIterator(getPathIterator(at), flatness);
}
/**
* Creates a new shape of the same run-time type with the same contents
* as this one.
*
* @return the clone
*
* @exception OutOfMemoryError If there is not enough memory available.
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public Object clone()
{
// This class is final; no need to use super.clone().
return new GeneralPath(this);
}
/**
* Helper method - ensure the size of the data arrays,
* otherwise, reallocate new ones twice the size
*
* @param size the minimum array size.
*/
private void ensureSize(int size)
{
if (subpath < 0)
throw new IllegalPathStateException("need initial moveto");
if (size <= xpoints.length)
return;
byte[] b = new byte[types.length << 1];
System.arraycopy(types, 0, b, 0, index);
types = b;
float[] f = new float[xpoints.length << 1];
System.arraycopy(xpoints, 0, f, 0, index);
xpoints = f;
f = new float[ypoints.length << 1];
System.arraycopy(ypoints, 0, f, 0, index);
ypoints = f;
}
/**
* Helper method - Get the total number of intersections from (x,y) along
* a given axis, within a given distance.
*/
private int getAxisIntersections(double x, double y, boolean useYaxis,
double distance)
{
return (evaluateCrossings(x, y, false, useYaxis, distance));
}
/**
* Helper method - returns the winding number of a point.
*/
private int getWindingNumber(double x, double y)
{
/* Evaluate the crossings from x,y to infinity on the y axis (arbitrary
choice). Note that we don't actually use Double.INFINITY, since that's
slower, and may cause problems. */
return (evaluateCrossings(x, y, true, true, BIG_VALUE));
}
/**
* Helper method - evaluates the number of intersections on an axis from
* the point (x,y) to the point (x,y+distance) or (x+distance,y).
* @param x x coordinate.
* @param y y coordinate.
* @param neg True if opposite-directed intersections should cancel,
* false to sum all intersections.
* @param useYaxis Use the Y axis, false uses the X axis.
* @param distance Interval from (x,y) on the selected axis to find
* intersections.
*/
private int evaluateCrossings(double x, double y, boolean neg,
boolean useYaxis, double distance)
{
float cx = 0.0f;
float cy = 0.0f;
float firstx = 0.0f;
float firsty = 0.0f;
int negative = (neg) ? -1 : 1;
double x0;
double x1;
double x2;
double x3;
double y0;
double y1;
double y2;
double y3;
double[] r = new double[4];
int nRoots;
double epsilon = 0.0;
int pos = 0;
int windingNumber = 0;
boolean pathStarted = false;
if (index == 0)
return (0);
if (useYaxis)
{
float[] swap1;
swap1 = ypoints;
ypoints = xpoints;
xpoints = swap1;
double swap2;
swap2 = y;
y = x;
x = swap2;
}
/* Get a value which is hopefully small but not insignificant relative
the path. */
epsilon = ypoints[0] * 1E-7;
if(epsilon == 0)
epsilon = 1E-7;
pos = 0;
while (pos < index)
{
switch (types[pos])
{
case PathIterator.SEG_MOVETO:
if (pathStarted) // close old path
{
x0 = cx;
y0 = cy;
x1 = firstx;
y1 = firsty;
if (y0 == 0.0)
y0 -= epsilon;
if (y1 == 0.0)
y1 -= epsilon;
if (Line2D.linesIntersect(x0, y0, x1, y1,
epsilon, 0.0, distance, 0.0))
windingNumber += (y1 < y0) ? 1 : negative;
cx = firstx;
cy = firsty;
}
cx = firstx = xpoints[pos] - (float) x;
cy = firsty = ypoints[pos++] - (float) y;
pathStarted = true;
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_CLOSE:
x0 = cx;
y0 = cy;
x1 = firstx;
y1 = firsty;
if (y0 == 0.0)
y0 -= epsilon;
if (y1 == 0.0)
y1 -= epsilon;
if (Line2D.linesIntersect(x0, y0, x1, y1,
epsilon, 0.0, distance, 0.0))
windingNumber += (y1 < y0) ? 1 : negative;
cx = firstx;
cy = firsty;
pos++;
pathStarted = false;
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_LINETO:
x0 = cx;
y0 = cy;
x1 = xpoints[pos] - (float) x;
y1 = ypoints[pos++] - (float) y;
if (y0 == 0.0)
y0 -= epsilon;
if (y1 == 0.0)
y1 -= epsilon;
if (Line2D.linesIntersect(x0, y0, x1, y1,
epsilon, 0.0, distance, 0.0))
windingNumber += (y1 < y0) ? 1 : negative;
cx = xpoints[pos - 1] - (float) x;
cy = ypoints[pos - 1] - (float) y;
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_QUADTO:
x0 = cx;
y0 = cy;
x1 = xpoints[pos] - x;
y1 = ypoints[pos++] - y;
x2 = xpoints[pos] - x;
y2 = ypoints[pos++] - y;
/* check if curve may intersect X+ axis. */
if ((x0 > 0.0 || x1 > 0.0 || x2 > 0.0)
&& (y0 * y1 <= 0 || y1 * y2 <= 0))
{
if (y0 == 0.0)
y0 -= epsilon;
if (y2 == 0.0)
y2 -= epsilon;
r[0] = y0;
r[1] = 2 * (y1 - y0);
r[2] = (y2 - 2 * y1 + y0);
/* degenerate roots (=tangent points) do not
contribute to the winding number. */
if ((nRoots = QuadCurve2D.solveQuadratic(r)) == 2)
for (int i = 0; i < nRoots; i++)
{
float t = (float) r[i];
if (t > 0.0f && t < 1.0f)
{
double crossing = t * t * (x2 - 2 * x1 + x0)
+ 2 * t * (x1 - x0) + x0;
if (crossing >= 0.0 && crossing <= distance)
windingNumber += (2 * t * (y2 - 2 * y1 + y0)
+ 2 * (y1 - y0) < 0) ? 1 : negative;
}
}
}
cx = xpoints[pos - 1] - (float) x;
cy = ypoints[pos - 1] - (float) y;
break;
case PathIterator.SEG_CUBICTO:
x0 = cx;
y0 = cy;
x1 = xpoints[pos] - x;
y1 = ypoints[pos++] - y;
x2 = xpoints[pos] - x;
y2 = ypoints[pos++] - y;
x3 = xpoints[pos] - x;
y3 = ypoints[pos++] - y;
/* check if curve may intersect X+ axis. */
if ((x0 > 0.0 || x1 > 0.0 || x2 > 0.0 || x3 > 0.0)
&& (y0 * y1 <= 0 || y1 * y2 <= 0 || y2 * y3 <= 0))
{
if (y0 == 0.0)
y0 -= epsilon;
if (y3 == 0.0)
y3 -= epsilon;
r[0] = y0;
r[1] = 3 * (y1 - y0);
r[2] = 3 * (y2 + y0 - 2 * y1);
r[3] = y3 - 3 * y2 + 3 * y1 - y0;
if ((nRoots = CubicCurve2D.solveCubic(r)) != 0)
for (int i = 0; i < nRoots; i++)
{
float t = (float) r[i];
if (t > 0.0 && t < 1.0)
{
double crossing = -(t * t * t) * (x0 - 3 * x1
+ 3 * x2 - x3)
+ 3 * t * t * (x0 - 2 * x1 + x2)
+ 3 * t * (x1 - x0) + x0;
if (crossing >= 0 && crossing <= distance)
windingNumber += (3 * t * t * (y3 + 3 * y1
- 3 * y2 - y0)
+ 6 * t * (y0 - 2 * y1 + y2)
+ 3 * (y1 - y0) < 0) ? 1 : negative;
}
}
}
cx = xpoints[pos - 1] - (float) x;
cy = ypoints[pos - 1] - (float) y;
break;
}
}
// swap coordinates back
if (useYaxis)
{
float[] swap;
swap = ypoints;
ypoints = xpoints;
xpoints = swap;
}
return (windingNumber);
}
} // class GeneralPath